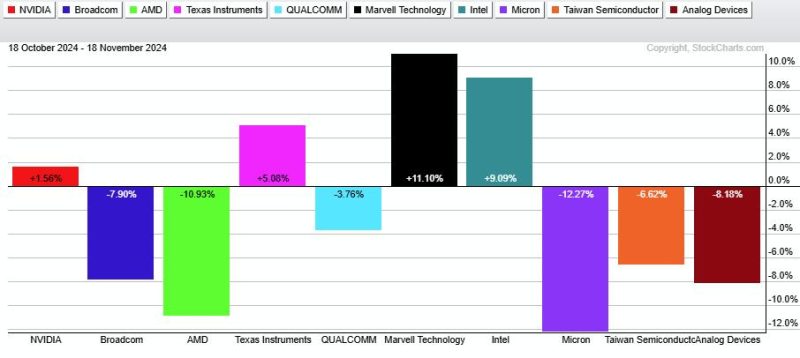
In the dynamic and rapidly evolving world of technology and investing, the performance of Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) tracking the semiconductor industry can provide valuable insights into market trends and sector sentiment. Two prominent ETFs in this space, the iShares PHLX Semiconductor ETF (SOXX) and the VanEck Vectors Semiconductor ETF (SMH), have been closely watched by investors and analysts alike due to their exposure to leading semiconductor companies. Despite sharing a common focus on the semiconductor industry, these two ETFs have exhibited differing performances during certain market conditions, leading to questions about the underlying factors driving their divergence.
One key factor contributing to the different performance of SMH and SOXX lies in their respective holdings. While both ETFs include prominent semiconductor companies such as Intel, NVIDIA, and Texas Instruments, the weighting of these companies within each fund differs significantly. SMH, for instance, has a more concentrated portfolio with its top holdings accounting for a larger percentage of the fund’s total assets compared to SOXX. This concentration can result in a higher level of correlation with the performance of key semiconductor stocks, potentially leading to more pronounced price movements in response to industry-specific news and events.
Additionally, differences in sector exposure and investment strategy between SMH and SOXX can also influence their performance relative to each other. SMH, for example, tracks the MVIS US Listed Semiconductor 25 Index, which includes companies primarily involved in the production of semiconductors and semiconductor equipment. In contrast, SOXX follows the PHLX SOX Semiconductor Sector Index, which encompasses a broader range of companies involved in various aspects of the semiconductor industry.
Moreover, market conditions and investor sentiment can play a significant role in the performance of semiconductor ETFs. Economic uncertainties, geopolitical tensions, and industry-specific developments can impact the semiconductor sector, leading to volatility in ETF prices. The relative resilience of SMH compared to SOXX during certain market downturns or sector-specific challenges may be attributed to differences in their respective holdings, sector exposure, and risk management strategies.
Ultimately, understanding the nuances of semiconductor ETFs such as SMH and SOXX requires a holistic analysis that considers factors such as holdings, sector exposure, investment strategy, and market dynamics. Investors seeking exposure to the semiconductor industry through ETFs should conduct thorough research, evaluate their risk tolerance and investment objectives, and consider consulting with financial professionals to make informed decisions. By staying informed and vigilant, investors can navigate the complexities of the semiconductor sector and position themselves for long-term success in the ever-changing world of technology and investing.